HOCD ranks among the most complicated psychological problems because of its chronic nature and tendency to aggravate mental health issues when not treated timely. Studies have shown that it is common among individuals with OCD and associated with clinical characteristics like restlessness, aggressiveness, impulsive behaviour and anxiety, with males twice as likely to be affected than females.
The good news is with care and therapy; you can get rid of HOCD to a large extent. Whether you get rid of HOCD permanently depends on how effectively you respond to the treatment.
Before learning about treatment options for HOCD, you should understand that it is a form of OCD with similar symptoms. Treatment of HOCD usually combines education about sexuality and OCD with OCD treatments like relaxation techniques, cognitive restructuring, mindfulness training and pharmacology.
Let’s discuss them in brief.
Relaxation techniques
Relaxation techniques help people experience their breath and body and give the mind time to relax. This works on reducing the feeling of overwhelmingness, which is a common symptom of OCD and HOCD patients. A meta-analysis of 16 trials conducted by a Korean team of researchers has shown that combining meditation-based techniques and medications is more effective than only medications in patients with OCD symptoms.
Some of the chief relaxation techniques are
- Deep breathing
Slow Breathing Exercises keep your attention on breathing and keep your mind off compulsive thoughts. Research has shown that deep breathing increases serotonin levels in the body, which lowers the stress levels common in HOCD and OCD.
Among the numerous deep breathing techniques, the most popular is the 4-7-8 technique, in which you breathe in for four seconds, keep your breath for seven seconds and breathe out for eight seconds.
5-3-3 is another technique in which you take five deep breaths in through the nose and out through the mouth and follow it with three quick breaths similarly.
- Mindfulness Meditation
Mindfulness Meditation combines meditation with mindfulness which is the practice of becoming more fully aware of the present moment. Mindfulness meditation teaches you to slow down overthinking and calm your body and mind. Studies have shown that mindfulness meditation lowers the heart rate and reduces stress, both of which are impacted in OCD patients.
To practice mindful meditation, sit straight in a comfortable position with your feet on the floor and hands in your lap. Breathe through your nose and focus on your breath moving in and out of your body. If you are interrupted because of unwanted thoughts or physical interference, gently get your focus back and continue with your breathing exercise.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation
It is known that the body responds to stress with muscle tension in the form of tightness or spasms that can be painful and uncomfortable for the person. A tensed muscle relays to the body that it is stressed and starts the cycle of stress and muscle tension. Progressive muscle relaxation breaks this cycle and reduces muscle tension in the body. It even works on anxiety levels with disrupted sleep patterns and improves the quality of life.
To practice PMR, lie or sit in a comfortable position in a suitable positive environment and take a slow deep breath. As in your inhale, clench all of the muscles in your face. Hold this for 10 to 20 seconds, then release the tension while slowly exhaling.
You can even try a Visualization form of relaxation and form mental images of the things that make you happy to calm down and release pent-up energy. For practising visualization technique, close your eyes and visualize a situation while including other senses like smell, touch and taste. E.g., if ice cream makes you happy, imagine a cup of your favourite ice cream and think about its cool touch on your fingers and taste while closing your eyes.
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
Cognitive Behavior Therapy involves recognizing unhealthy thought patterns and replacing them with positive/neutral thinking. In HOCD and OCD patients, cognitive behaviour therapy is considered the first line of treatment because of its proven effectiveness in providing long-term results for the problem.
Multiple sessions are conducted for the CBT method in which your thinking patterns and problematic behaviours are identified while keeping in mind your life experiences from childhood until adulthood. Based on the information provided, the psychologist forms a picture of your situation and refines it as they obtain more information in each visit.
You are then made to understand the impact of your thoughts on your behaviour and counselled on the necessary behavioural changes to adopt a realistic, rational perspective. Some of the basic Cognitive Behavior Techniques are
- Exposure and Response Prevention
In this method, you are provoked and exposed to situations in a safe environment to face your fears and make a choice that would help your therapy.
- Cognitive Restructuring
In Cognitive Restructuring Therapy, the psychoanalyst/psychiatrist helps you identify ineffective patterns in your thinking and counsels you on the correct way to change them to prevent the recurrent triggers of negative emotions caused by HOCD.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy helps you heal from the trauma caused by HOCD triggers and move on instead of dwelling on the negative emotions/thoughts and changing your feelings.
- Role-Playing
In a role-playing method, the therapist puts themselves in your shoes to understand your problem in a better manner and guide you appropriately. Alternatively, in role-playing, the therapist takes the role of someone you are afraid to confront, and you need to talk with them to heal.
- Worst case/ Best case/ Most likely Scenario
In this method, you are made to identify your worst case or scenario and create possibilities for getting out / remedying it into an outcome that is either the best solution or the most likely approach to dealing with it.

Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation is a surgical treatment condition preferred for patients in a chronic stage of HOCD who are not responding to other modalities. In this method, the physician first conducts an ECG to locate the part of your brain involved in the neurotransmitter imbalance activity.

After identification, they implant two electrodes in the affected area and attach a neurostimulator to your collarbone to deliver mild electric signals. Then they connect the electrodes to the neurostimulator to send electrical signals to the brain to activate the axon terminals and release neurotransmitters like GABA, dopamine, serotonin and glutamate that will balance the neurotransmitter triggers for OCD.
Deep Brain Stimulation is regarded as an effective treatment option and is said to produce positive results in almost 60% of patients undergoing the therapy. It won’t cure the disease outright but will stimulate the natural production of neurotransmitters that will significantly decrease the intensity of HOCD symptoms.
DBS is a possible treatment method only if you have had severe HOCD for at least five years and did not obtain successful results even after 25 rounds of Cognitive Therapy or SSRIs after 12 weeks. Additionally, elderly patients or those with advanced dementia are not deemed eligible for the surgery.
You can observe noticeable results in a short time after surgery. The effects last several years but are not permanent and may need to be supplemented with SSRIs or psychotherapy.
Pharmacology
Medications are not the primary treatment options for HOCD; they are usually advised as a combination treatment option for better results or when psychotherapy does not produce satisfactory results. Owing to the absence of a formal diagnosis of the condition, it is treated as a complex subtype of OCD and treatment is conducted along similar lines.
SSRIs ( Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) and tricyclic antidepressants like Clomipramine are the primary pharmacological interventions in HOCD conditions that keep obsessions and compulsive behaviour in check.
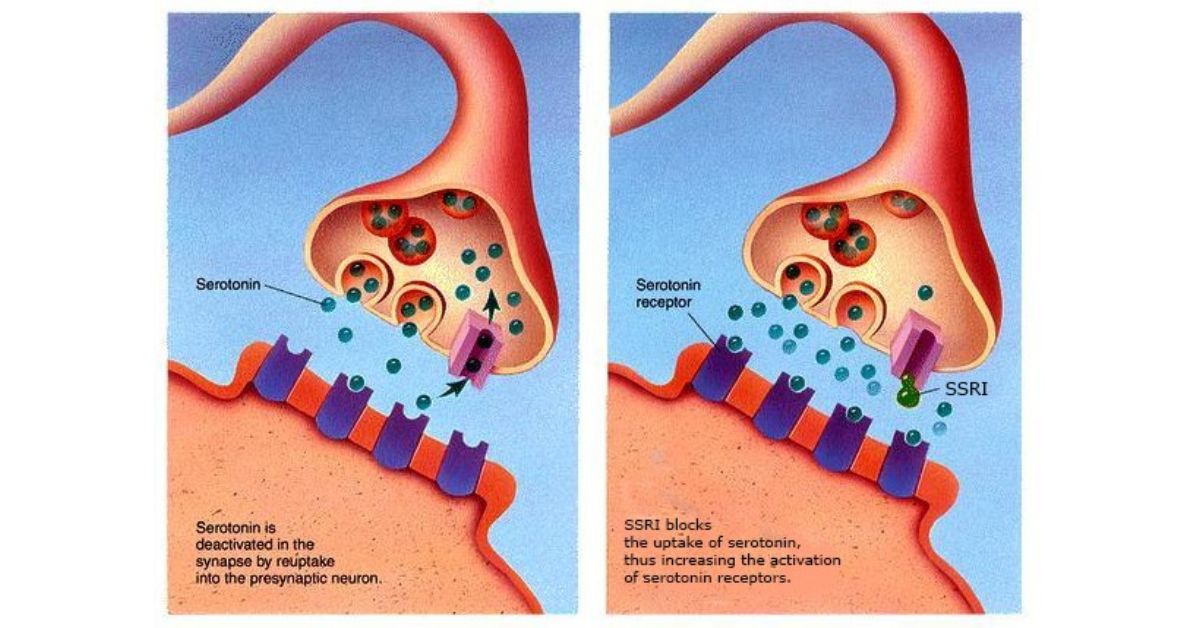
Studies conducted on OCD patients have shown an imbalance in serotonin synthesis capacity to be a major reason behind the problem. The popularity of SSRI s stems from the fact that SSRIs improve the serotonin levels in the brain to improve OCD-induced compulsive behaviours to a moderate extent. Fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, sertraline, or citalopram are some primary medications for OCD patients. Based on the physician’s advice, they can be used in modified doses for HOCD patients.

In conditions of SSRi intolerance SNRIs ( Serotonin Nor-Epinephrine Inhibitors ) like Venlafaxine is the preferred option.
Diagnosis of HOCD
One of the chief problems clinicians face in treating HOCD is formally diagnosing the term not mentioned in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. It is recognized as a subtype of OCD, and treatment options are initiated to treat the OCD symptoms in HOCD patients that fortunately coincide with the chief problem. Because of the indirect approach to diagnosing the problem, HOCD is confused with other symptoms like Denial, even when HOCD and Denial are two different phenomena with variable parameters regarding homosexuality.
In a study conducted to better understand the concept of HOCD and correlate it with OCD, researchers conducted a retrospective review of the patients seen in three years at the McGill University Sexual Identity Centre. A total of 6 cases were found, out of which four were diagnosed as HOCD and researched. Young men with limited sexual relations were primarily included in the study who, in addition to being shy, had a sub-clinical threshold of obsessional history in the past.
The obsessional doubt regarding their sexual orientation was very distressing for all the subjects. Unlike homosexual individuals who are initially unsure about their sexuality but improve their confidence in due course, in HOCD, the symptoms did not lessen with time. All the patients presented with symptoms of mental compulsions, avoidance and continuous internal debate about their sexual orientation that was in line with a mental compulsion. Judging on the similarity of patterns, the study concluded that HOCD and OCD were of a similar origin and that diagnosis and treatment options should be identical in either condition.
Conclusion
Obsessive–compulsive disorder is ranked by the WHO as among the ten most debilitating conditions and tends to be chronic when not treated in time. While it is impossible to know whether your fears are valid, the agony of not knowing creates such a situation that people opt to go through extreme life changes like changing cities and quitting jobs to avoid potential triggers. And the worst part is nothing can cure HOCD permanently. Treatment measures decrease the intensity of symptoms and provide symptomatic relief to the patient. But the problem can persist or return after being suppressed through therapy.
In such conditions, Cognitive Behaviour therapy is regarded as the most effective treatment option for HOCD. Some clinicians deem Cognitive Behavior Therapy the only treatment option because of its certainty of results and non-invasive approach, resulting in increased safety. CBT and serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are recommended as safe and effective first-line treatments for OCD.
Whether to utilize CBT, an SRI, or combined treatment will depend on factors that include the nature and severity of the patient’s symptoms, the nature of any co-occurring psychiatric and medical conditions and their treatments, the availability of CBT, and the patient’s past treatment history, current medications, capacities, and preferences.
