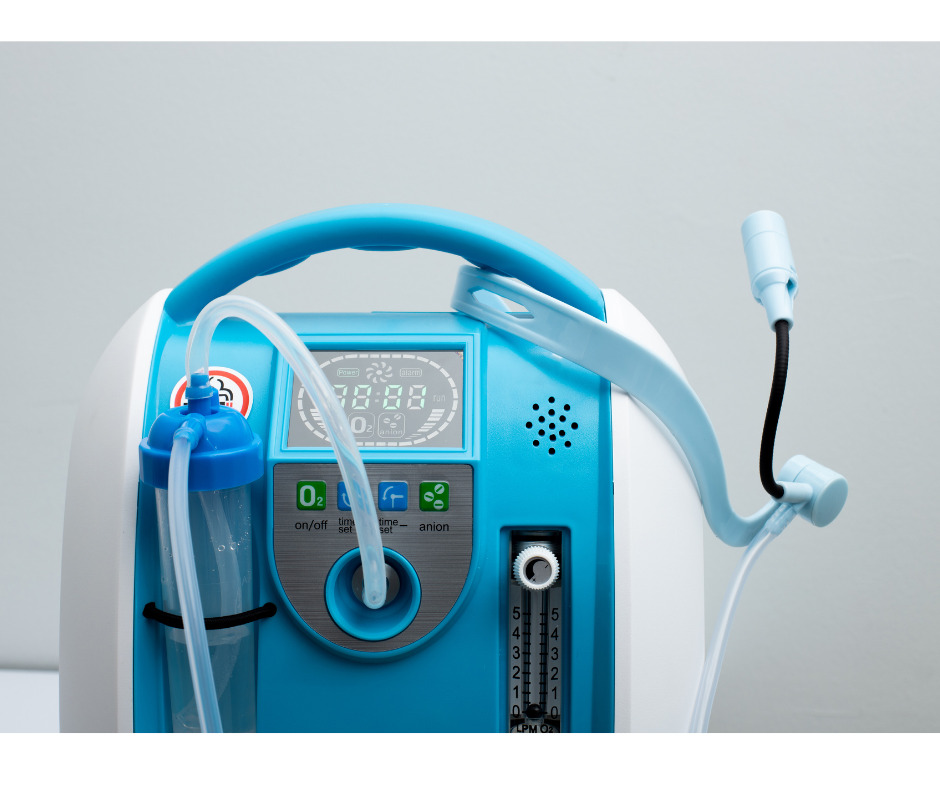
Oxygen concentrator
An oxygen concentrator is a device that selectively absorbs the oxygen from the surrounding air by removing nitrogen from it. It is used on patients with decreased oxygen levels in the blood. These days of the ongoing pandemic, it is popularly used as an oxygen supplement by patients with respiratory disorders.
When do you need an oxygen concentrator?
The medical condition that causes problems in breathing requires an oxygen concentrator. When the lungs can’t absorb oxygen on their own, they need to be supplemented with oxygen from outside. Any pulmonary disease like COPD(Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, a serious asthma attack, pneumonia, or cystic fibrosis(a genetic disorder of the lungs) making it important for the lungs to depend on external oxygen.
Is it the same as an oxygen tank?
Many people confuse it with being a sophisticated version of an oxygen tank. But it is not the fact. Oxygen tanks are oxygen cylinders containing a limited amount of oxygen. They can be used as long as the oxygen amount in the cylinder does not run out. After this, the empty cylinder becomes useless, and a new oxygen cylinder has to be provided or the cylinder refilled with oxygen.
On the other hand, oxygen concentrators are built to take oxygen from the surrounding air because of which they work for a much longer time than the cylinders. In simpler terms, they can filter unlimited oxygen from the surrounding till their battery runs out which is a long time.
How does an oxygen concentrator work?

There are 2 ways in which oxygen concentrator’s work.
1) Pressure Swing Adsorption
2) Membrane Gas Separation
Pressure Swing Adsorption
Pressure Swing Adsorption works on the theory of “Adsorption” or Attraction of Gases to Solids. In this method, the air is passed through an adsorbent bed of zeolite. This attracts nitrogen more efficiently than oxygen. The result being nitrogen stays in bed, and the air that comes out is rich in oxygen.
Apart from zeolite, other adsorbents like silica gel, alumina, and activated carbon are also used. Because it works on the pressure equalization system, the power consumption and energy-saving are on the lower side, making it a popular technique.
Membrane Gas Separation
Membrane Gas Separation works on the theory of Robeson Limit. The factor states that permeability and selectivity are inversely proportional to each other. In this method, has mixtures are separated by synthetic membranes made from polymers like polyamide or cellulose acetate and even ceramic materials.
Air is separated based on solubility and diffusivity. Oxygen is separated and released from the upstream side, while nitrogen is collected at the downstream side. This method is cost-effective as well as environmentally friendly because of the use of non-toxic materials.
Factors to consider before you buy an oxygen concentrator from Amazon
Flow requirement
Flow requirement is the oxygen flow per minute (1-6l/min). At an oxygen flow rate of 2l/ min, the oxygen concentration in the lungs reaches 25-30% against their maximum capacity of 95-100%. And the oxygen saturation level (the amount of oxygen in the bloodstream) needs to be 95-100%.
The flow rate is around 0.5 liters/ minute because the comparatively lower flow of oxygen concentrators is suitable for oxygen saturation levels between 92-94. If the saturation level falls below 92, it’s time to switch to an oxygen cylinder with 2 liters/minute flow rate.
Age
It can be used on any age group, from a one-year-old baby to an 82-year-old adult, as long as it comes with a doctor’s prescription.
Doctors prescription
Yes, we do need a doctor’s prescription for getting an oxygen concentrator. Two people with the same medical conditions have a very good chance of having different oxygen levels in the body. Your physician needs to be sure about your oxygen levels before deciding which one do you need.
Only after doing your ABG test (Arterial blood gas) and checking your oxygen through a pulse oximeter is the decision whether you need a pulse concentrator or a continuous flow concentrator.
Size
Oxygen concentrators come in 3 sizes. We can understand it better with the help of a small chart.
| Size | length (inches) | weight | capacity | saturation capacity | concentration |
| small | 6.4*4.8 | 250-500gm | 330ml | 0.5litres/min | 93-94 |
| medium | 10.2*8.6 | 700-850gm | 3-5litres | 0.5litres/min | 92-94 |
| large | 14.2*15 | 7kg | 8-10litres | 1-6litres/min | 92-94 |
Cost
The cost of a concentrator varies from 500$ – 2000 $ depending on the machine’s size, portability oxygen capacity.
A used concentrator in working condition can be bought from 300$ to 1200$, depending on the warranty and condition of the machine.
Types
Oxygen concentrators are of 2 types. Portable concentrators and Stationary Concentrators (Also called Home Concentrators).
Portable oxygen concentrators
Portable oxygen concentrators can be either Pulse Units or Continuous Units.
Pulse oxygen concentrators are designed for people who can move around wearing them. It is based on your breathing rate and the intensity of each breath. It can detect when we will take our next breath and deliver a bolus or pulse of oxygen. Likewise, it can detect when we will breathe more intensely and supply a higher pulse of oxygen. It is small and compact, along with being easy to handle.
Continuous oxygen concentrator, on the other hand, is not dependent on our breathing. They once plugged in, continue to provide oxygen irrespective of our activity and breathing. They are more convenient for nighttime use. Because then the breathing becomes shallow and pulse concentrators might not be as effective.
Stationary Concentrators
On the other hand, stationary concentrators are of two types: The medium-sized having a flow of 5LPM; or the Higher Flow units having a flow of 8-10LPM. It depends on the needs and medical condition of the patient, along with the prescription of the practitioner regarding the best one for him. These concentrators work on electricity and need to be connected with inverters in case of power cuts.
Use Duration
One liter of oxygen causes around a 24% increase in oxygen in the lungs. With 2 liters, the percentage of oxygen increases to 28%, with 5-10litres around 50%. It might be a boon for people who need more oxygen, but excess oxygen can lead to “Oxygen Toxicity” in the body. Unfortunately, oxygen toxicity causes irreversible damage to the lungs and C.N.S because of which concentrators should be used only in the doses and duration that the physician recommends.
Pros and cons of the oxygen concentrator
Pros
Unlimited oxygen
Oxygen cylinders come with limited oxygen capacity. After depletion, the empty cylinders are useless or need to be refilled for further use. Oxygen concentrators, on the other hand, take oxygen directly from the air. This makes their supply unlimited, which makes them more reliable in case of emergencies.
Easily Available
The current situation has caused an extreme shortage of cylinders throughout the world. The difficulty is more so because of the limited reserve of the cylinders. Oxygen concentrators, in comparison, are readily available and useful in a variety of breathing disorders because of their versatility.
Versatile
Oxygen cylinders come in only one model with the size depending on the requirement. Concentrators come in a variety of designs, from pulse models to continuous models and sizes depending on the oxygen requirements. This makes concentrators more versatile than cylinders with being more user-friendly.
Portable
Cylinders are heavy. An average cylinder weighs around 60kgs along with lasting for less than 6 hours. Along with providing unlimited oxygen, a portable concentrator is lightweight as well. Making it a welcome and lighter alternative.
Safer
There is always a risk of leakage of oxygen from the cylinders resulting in a fire accident. There is no such issue in concentrators where they take the air and convert it to medical quality oxygen instead of storing it inside.
Cons
As with pros, there are cons associated with concentrators as well which must be taken into consideration.
Battery or Power dependent
Unlike oxygen pumps that do not require a power backup, concentrators depend on a battery or electricity to keep them working. Thus in case of power cuts, connecting them to an inverter or keeping a spare cylinder becomes vital for the patient’s health.
Makes more noise
They make noise mostly because of the valves in their compressor. There are rubber mounts designed to absorb the noises of the compressor. But in they wear out or crack, making a lot of noise while operating.
Less effective
The flow rate is approximately 0.5 LPM which means they can be used for mild cases, i.e., as long as the oxygen saturation is 92 and in worst cases 85. Beyond that, their efficacy decreases, and a pump becomes extremely crucial to avoid complications.
Expensive
Concentrator costs around 1200$ compared to a cylinder that comes at less than 1/3rd of its price. That, with the setup and maintenance needs, makes them pretty expensive to buy and maintain.
Risk of infection
There is a greater risk of infection in concentrators because of the improper distilled water used in the humidifiers. There is a comparatively lesser chance of infections in cylinders because of their uncomplex mechanism.
Important things to remember while using an oxygen concentrator

Do not keep them near inflammable substances
Oxygen is a highly inflammable gas. It is very important to keep the concentrator away from inflammable substances to prevent fire accidents from occurring.
Do not smoke near them
Apart from the risk of a fire, the smoke is a big no for a patient with already lung problems. Do not smoke near a concentrator. Put no-smoking posters around them if necessary to make it clear that this has to be taken seriously.
Do not use petroleum-based products near them
Some creams contain petroleum which is a highly inflammable substance. Do not use creams or products containing petroleum near a concentrator.
Do not overuse them
Try to reduce their use as much as possible. Apart from weakening our lungs when used long-term, there is also a possibility of oxygen toxicity overusing them.
Always keep a pump ready in case of emergencies
Anything may happen. There might be a power cut, and the batteries may stop working. Always keep a cylinder handy in case of unforeseen emergencies.
The current circumstances make it necessary to use oxygen concentrators when the need arises. But learning how to set them and handle any problems associated with their use is important as well. Take the utmost care when using them. As soon as the situation permits, gradually lessen their use to better your lungs and overall body.